Key Takeaways
- Access control is essential for protecting data and preventing unauthorized access.
- Implementing robust access control strategies can address various security challenges faced by organizations.
- Diverse access control models, such as role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based acc ess control (ABAC), offer flexibility and effectiveness.
- Emerging technologies are enhancing access control systems, making them more secure and user-friendly.
Introduction
In today’s digital world, security is paramount for individuals and organizations. Threats from hackers who take advantage of weaknesses to obtain unauthorized access to private data are growing along with technology. One essential element of cybersecurity, acce ss control, provides a straightforward yet effective way to reduce these threats. Acce ss control helps organizations protect their information and reputation by efficiently controlling who can access or interact with systems, data, and resources. This post will examine how acce ss control offers a simple solution to typical security issues.

Understanding Access Control
The process of limiting access to resources so that only systems or people with permission can use them is known as acce ss control. This idea, essential to security frameworks, attempts to shield private information from unwanted access. Access control mechanisms come in various forms, from simple password protections to more sophisticated models that leverage advanced technologies. Regardless of complexity, the underlying principle remains the same: ensuring that only those with the proper credentials can access specific information or systems. As threats evolve, organizations must continually adapt their acce ss control strategies to stay ahead of potential security breaches.
Types of Access Control Models
Several access control models have been developed for security needs and operational environments. The three most common models are:
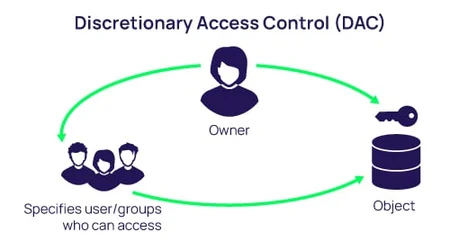
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
DAC grants resource owners the discretion to set user permissions. This model offers flexibility but can be prone to human error, leading to improper permissions and potential security gaps if not managed meticulously.
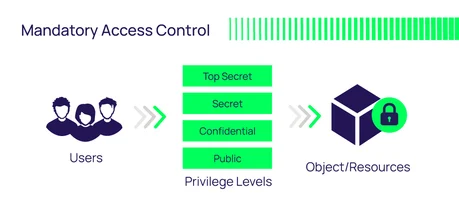
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
MAC enforces strict policies set by a central authority, removing DAC’s flexibility but increasing security. This model is typically used in environments where data classification and security are of the utmost importance, such as military or government networks.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC allows users access only the resources required for their job duties by allocating permissions according to user roles within an organization. This approach simplifies permission management and enhances security by minimizing unnecessary access.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
ABAC evaluates various attributes, such as user role, location, and the data in question, to determine access permissions. It offers a dynamic and fine-grained approach to acce ss control, allowing for more nuanced permission settings.
The Benefits of Access Control
Implementing a robust access control system brings numerous benefits to organizations:
Enhanced Data Protection
Acc ess control dramatically lowers the risk of data breaches by guaranteeing that only authorized individuals can access critical information. Organizations can safeguard their intellectual property and confidential data, maintaining client trust and avoiding reputational damage.
Compliance with Regulations
Several businesses are subject to regulations requiring strict data protection procedures. Acc ess control helps organizations meet these obligations by providing a structured data access and protection framework.
Streamlined Operations
Efficiently managing user permissions through access control systems reduces administrative overhead and minimizes human errors. Automated processes enable quick adjustments to user roles and permissions, facilitating seamless operations.
Reduced Insider Threats
Access control reduces the danger of insider attacks by limiting user access to what is required for their tasks. It also enables tracking and monitoring user activities, allowing quicker identification and response to suspicious behavior.
Challenges in Implementing Access Control
While acc ess control is essential to cybersecurity, it can be challenging. Organizations must navigate several hurdles to establish an efficient system:
Balancing Security and Usability
It can be challenging to strike the ideal mix between strong security features and user comfort. While inadequate controls may expose firms to security concerns, too rigorous controls can impede productivity. It takes careful preparation and constant assessment to achieve this balance.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating access control systems with existing IT infrastructure can be complex and requires significant resources. Organizations may face compatibility issues, especially when dealing with legacy systems that need more modern security features.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Because cybersecurity risks are ever-changing, access control systems must be continuously monitored and adjusted. Organizations must also periodically evaluate and update their policies to manage emerging risks effectively.
Leveraging Emerging Technologies for Access Control
Advancements in technology offer opportunities to enhance acc ess control systems, making them more secure and user-friendly.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies are being integrated into accmess control systems to automate complex processes, such as risk assessment and threat detection. These systems can analyze behavioral patterns and detect anomalies, enabling proactive threat management.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric technologies—like fingerprint and facial recognition—offer high security by using distinctive bodily traits for verification. Biometric authentication reduces reliance on passwords, decreasing the risk of credential-based attacks.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain offers a decentralized and tamper-proof method for managing access control logs. It ensures transparency and integrity by allowing authorized parties to verify access events, enhancing accountability and auditability.
Implementing Effective Access Control Strategies
Organizations can follow these best practices to implement effective access control systems:
- Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities and prioritize resources.
- Develop a detailed acce nss control policy aligned with organizational goals and security requirements.
- Implement multi-factor authentication to enhance security and reduce dependence on passwords.
- Regularly review and update access permissions to reflect user roles and responsibilities changes.
- Educate employees about access control protocols and the importance of security measures.
Conclusion
Acce ss control is an indispensable tool in the cybersecurity arsenal, offering a simple yet powerful solution to common security challenges. By effectively managing resource access, organizations can protect sensitive data, comply with regulatory requirements, streamline operations, and reduce insider threats. While implementation may present particular challenges, leveraging emerging technologies and following best practices can enhance the effectiveness of acce ss control systems. As cyber threats change, organizations must be alert and flexible, honing their acce ss control tactics to strengthen their defenses and protect their digital assets.

